In today’s intricate food supply chain, the importance of food quality control is rapidly increasing. With food production, packaging, and shipping spanning vast distances to reach distant countries, upholding high-quality standards has become increasingly challenging.
Whether you’re a food manufacturer or an importer of food products, establishing and implementing an effective quality management system is crucial. In this article, we’ll provide an overview of highly effective food quality management methods.
What Is Food Quality Control?
Food quality control in food industry is monitoring and verifying food product quality throughout the supply chain – from actual production and shipment to before consumption – through systematic procedures. The ultimate goal is to verify that products meet stringent criteria for safety, taste, appearance, and other factors.
How Do We Maintain High Food Quality Standards?
There are various food safety requirements and several food safety and quality control regulations mandated by law or by large retailers/chains operating within the food industry. The most common quality standard is the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), created to address food safety by analysing and controlling biological chemicals or physical hazards throughout the food supply chain. As well as implementing and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) in your food supply chain.
What Are Examples of Food Quality Control in Food Industry?
There are various ways to conduct food quality control, including supplier verification, inspecting the quality of the produce, implementation of good manufacturing practices, hazard analysis and critical control points for training and education.
In this article, we’ll focus on two commonly discussed aspects related to the export and import of food products, specifically supplier verifications and inspections.
What Is a Food Supplier Audit?
A food supplier audit assesses and verifies the safety, quality, and compliance of a food supplier’s operations, processes, and products against established requirements or guidelines, including yours. Typically, these audits are conducted by an impartial third-party inspection company that assesses the supplier based on various criteria.
Food Supplier Audit Checklist
- Company legality information
- Bank information
- Human resources
- Exportation capability
- Order management
However, the supplier audit may also encompass a more comprehensive assessment of the supplier’s factory and production.
Food Supplier Factory Checklist
- Company’s background
- Manpower
- Production capability
- Machinery, facilities, and equipment
- Food safety management systems (e.g., HACCP)
- The manufacturing process and production line
- In-house food quality management and quality systems, such as testing and inspection
- Management system and capability
- Environment
What Is a Food Inspection?
A food inspection evaluates and verifies whether the food conforms to quality, safety criteria and established requirements. The inspections are carried out by trained third-party inspection agencies at various points along the food supply chain. But when it comes to food products exports and imports, the inspections are typically carried out at:
- Before shipment: This takes place at the facility where the food products are produced, packaged, and prepared for shipment.
- Loading/Unloading Supervision: At the point of loading or unloading, such as in a warehouse or transportation hub
Pre-Shipment Inspection for Food Products
Let’s take a look at the key steps involved in conducting a pre-shipment inspection of food products.
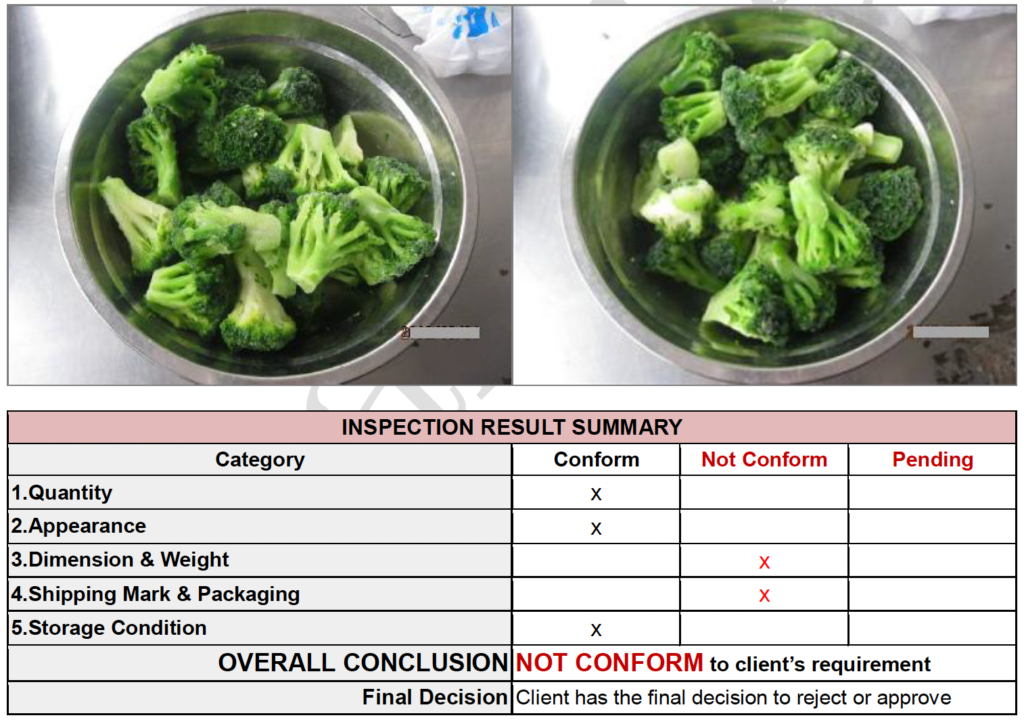
Quantity Verification
One of the crucial steps is to verify the quantity of the products. The inspector will check if the order quantity matches the order that was placed by the buyer. For example through counting (such as the number of units, boxes) or weighing the products (commonly used for larger orders) using calibrated scales or weighing equipment.

Overall Appearance
The inspector will assess the overall appearance of the food products, taking note of visual characteristics such as the colour, condition, size and shape to ensure that they conform to the required standards and are free from visible damages or abnormalities.
Dimensions and Weight
The inspector will measure the length, width, and height using different measuring tools or weigh the food products to compare the measurements and weight to the specified size requirement as per the purchase agreement or the contract.
Shipping Marks and Packaging
The inspector will in a pre shipment inspection of food assess whether the packaging is in good condition and appropriate for the type of food product being shipped. He or she will take note of different markings. For example, the product name, quantity, and country of origin, and evaluate compliance with applicable regulations and standards.
Storage Condition
Checking if the products have been stored properly in line with industry standards, including temperature and cleanliness. The inspector may also review record-keeping practices to ensure that proper documentation is maintained, such as temperature logs, product rotation records, and other records.
Note that specific inspection criteria may vary depending on buyer requirements, destination market, and type of products inspected.
What Is Food Testing?
There are multiple food quality testing services, ranging from assessing raw materials’ food quality and safety to finished products. Below, we’ve listed three common testing methods for food products.
- Microbiological Testing: Used to evaluate the levels of microorganisms in food products.
- Chemical Testing: Analyse the chemical components, such as nutrients, additives, and other substances.
- Physical Testing: Check the physical properties of a food product. For example, its texture, size, shape, and other relevant characteristics.
The Importance of Food Quality Control
Controlling the quality of food is important to ensure that consumers consume safe food products and safeguard them from risks associated with contaminated foods. For buyers, it also reduces the risks of dealing with fraudulent suppliers and receiving poor goods. Moreover, it ensures compliance with food laws and regulations, including food safety, labelling, and packaging requirements.
Conclusion: Food Quality Control: A Guide to Audits, Inspections and More
In today’s global food industry, ensuring food quality and safety is of paramount importance. In this article, we’ve outlined some effective food quality control methods for importers/exporters of food products, including audits, food inspections and testing for food and agricultural.
At HQTS, we’ve got over 25+ years of experience in quality assurance and can help your business with food safety audits and quality inspections at any point of your food supply chain. With coverage across 80+ countries, we can help you in virtually any part of the world. Contact us today to find out how we can help you navigate food quality control challenges.





