Uganda, located in East Africa, is projected to be among the fastest-growing economies by 2030. Driven by population growth and liberation of the economy since 1986, Uganda has seen accelerated economic growth, growing annually by over 6% over the past 30 years.
There are many opportunities for companies to export their goods to Uganda. However, similar to other East African countries, there are regulations that exporters need to be aware of, including that several products are regulated under Uganda’s Pre-Export Verification of Conformity programme, implemented by the Uganda National Bureau of Standards (UNBS).
In this guide, we’ll introduce the Uganda market and explain all the compliance regulations you need to be aware of when trading with this fast-growing country.
Uganda Market: A Quick Overview
Uganda is a market-based economy and one of the world’s fastest-growing economies. The country is rich in natural resources, with agriculture being the primary sector. The GDP has been forecasted to be $45.7 billion by 2021/22, and 68% of the population work in the agriculture industry.
The agricultural industry accounts for a large share of Uganda’s export earnings, which are mainly from coffee, fish, cotton, tea and gold. According to the Uganda Bureau of Statistics (UBOS) data, the top exporting goods and services from Uganda were to the United Arab Emirates ($1.05 billion), Kenya ($534 million), and South Sudan ($481 million),
Because of the dominance of the agricultural sector, the major manufacturing industries are often based on processing agricultural products, including coffee, tobacco, tea, grains, edible oils, and more. But since the 1990s, many foreign companies have invested in textile, steel mills, cement factories, car assembly plants, and metal and steel productions.
What Is the Biggest Import in Uganda?
The UBPS data from 2021 show that the top three importing goods and services to Uganda were in the following order: China ($1.3 billion), India ($841 million), and Tanzania ($811 million).
Meanwhile, the top three products imported from Uganda are:
- Petroleum, petroleum products and related materials
- Gold, non-monetary (excl. gold ores and concentrates)
- Road vehicles (including air-cushion vehicles)
See below for more detailed information.

What Can I Export From India to Uganda?
The bilateral trade between Uganda and India is strong, and the Indian community has over 35,000 Indians living in Uganda, concentrated in Kampala and in the town of Jinja. They play a leading role in the Ugandan economy.
Naturally, there is a big trade between Uganda and India. According to OEC, India exported goods to Uganda worth $797M USD in 2020. The main products that Uganda imported from India were: packaged medicines, refined petroleum, motorcycles and cycles, machinery, and plastic and plastic products.
Keep in mind that certain products are prohibited or restricted for import, including pornographic materials, used computers and appliances, used underwear, and used tires. In addition, Uganda has a Pre-Export Verification of Conformity program where your goods may require a certificate of conformity to enter the Ugandan market.
What Is the Uganda PVoC?
The Uganda Pre-Export Verification of Conformity is a programme operated by the Uganda Bureau of Standards (UNBS) that regulates the import of certain products. This program is designed to ensure that the product being exported to Uganda meets certain quality standards and will not adversely affect the health or safety of people in Uganda.
What Products Are Covered by the PVoC?
The program covers 11 product categories and requires that every regulated product must have a Certificate of Conformity (CoC) certification issued by appointed inspection agents in the country of export. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in delays, penalties, or the shipment being returned.

Which Product Categories Are Exempt From PVoC?
There are a series of commodities that are exempt from the PVoC programme. Note that these commodities are instead subject to inspection at the destination. They include, but are not limited to:
- Raw materials used in manufacturing processes.
- Less than USD$2000 Freight on board value.
- Diplomatic cargo.
- Products that are locally produced from partnering states of the East African Community.
- Spare parts and industrial machinery used for the production line.
- Classified police, prisons and military hardware and equipment.
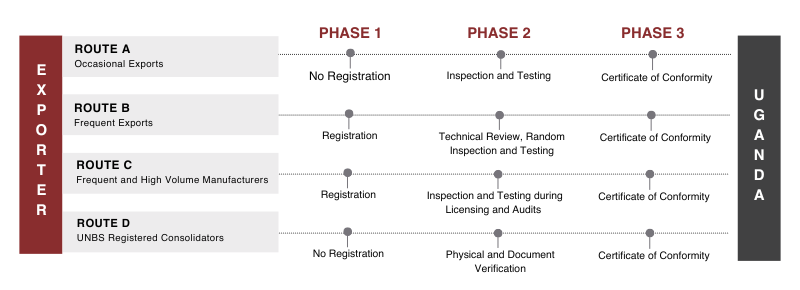
What Are the Routes for the Uganda CoC?
The process of certification will vary depending on the product category and the type of exports. There are four different certification routes.
Why Does Uganda Require a Certificate of Conformity?
The main reason is to prohibit the sale of substandard products and ensure that imported goods are safe for consumers. The certificate of conformity is issued by a contracted and independent third party to confirm that these products have been inspected and meet or exceed the required standards set by Uganda’s regulatory body.
What Are the Benefits of the PVoC to Uganda?
There are a series of benefits to complying with the Uganda PVoC programme, including:
- It is mandatory to comply with the Conformity Assessment Programme in Uganda.
- The certification will get you access to the Ugandan market.
- You will avoid customs delays.
- Reduce potential losses from importing non-compliant products.
Who Can Issue a Certificate of Conformity to Uganda?
The UNBS has contracted PVoC Services for General Goods to four independent third-party control companies, of which HQTS is one of them. At HQTS, we are authorised to issue Certificates of Conformity under the Uganda PVoC program for general goods. We can help you comply with UNBS regulations and experience a hassle-free export to Uganda. Do you want to export to Uganda? Contact us today to learn about our Uganda PVoC Services.





